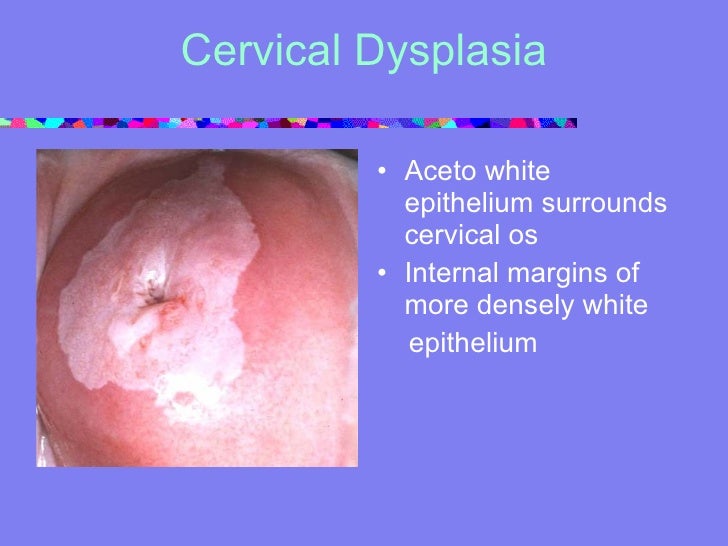
The test for detecting HPV is simpler than a Pap smear and, the study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found, it may be better at catching the earliest cervical cancer. Cervical cancer can often be cured if found early. Read about screening, using pap smears and testing for the HPV virus, which causes most cases. Cervical cancer can often be cured if found early. Read about screening, using pap smears and testing for the HPV virus, which causes most cases. Get Tested for Cervical Cancer Browse Sections. Overview; Cervical Cancer Screening for cervical cancer depends on how old you are and which screening tests you get. If you are age 21 to 29, get screened with a Pap test every 3 years. If you are having a Pap test and an HPV test, the doctor or nurse wont need to do an. Screening for cervical cancer using the Pap test has decreased the number of new cases of cervical cancer and the number of deaths due to cervical cancer since 1950. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the major risk factor for cervical cancer. Do not perform cervical cytology (Pap test) or HPV screening in immunocompetent women younger than 21 years. Pap smear, cytology, colposcopy, human papillomavirus, HPV, HPV testing, and HPV. The primary goal of cervical screening is to detect preinvasive cancers and prevent death from cervical cancer by treating precancerous lesions. There are a number of methods used to screen for cervical cancer precursors. Since cervical cancer is believed to be caused by sexually transmissible human papillomavirus infections, women who have not had sexual exposures (e. , virgins) are likely at low risk. Women aged 21 years who have not engaged in sexual intercourse may not need a. Updated Guidelines for Cervical Cancer Screening and Cervical Cancer and HPV Key to getting cancer: persistent HPV DNA tumor virus with over 150 genotypes Oncogenic HPV causes cervical cancer recommend HPV and Pap co. What is cervical cancer screening? Cervical cancer screening is used to find changes in the cells of the cervix that could lead to cancer. The cervix is the opening to the uterus and is located at the top of the vagina. Screening includes cervical cytology (also called the Pap test or Pap smear) and. The most comfortable and easy to use athome test for HPV, the virus that causes cervical cancer. Get accurate cervical cancer screening using an NHS endorsed testing method without having to visit your GP for a smear test But studies show that less frequent screening can still catch cancer early and that HPV testing needn't be done at the same time as a Pap test, said Dr. The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear, cervical smear, cervical screening or smear test) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb). Cervical screening is the process of detecting and removing abnormal tissue or cells in the cervix before cervical cancer develops. By aiming to detect and treat cervical neoplasia early on, cervical screening aims at secondary prevention of cervical cancer. Several screening methods for cervical cancer are the Pap test (also known as Pap smear or conventional cytology), liquidbased cytology. HPV Testing Alone Can Replace Pap Smear For Women Over 30: Shots Health News HPV testing is now seen as equally effective as Pap tests. HPV testing could one day replace pap smears, according to researchers. During a cervical screening, commonly known as a pap smear, a medical professional widens the vagina with a. A description of the NHS cervical screening programme, including evidence on screening for cancer and human papillomavirus (HPV) for women over 25. The new Cervical Screening Test is more accurate than the Pap smear test and the best test available for the prevention of most cases of cervical cancer. All women between the ages of 25 and 74 should have a HPV test every five years. New cervical cancer screening guidelines have been released by the U. Preventative Service Task Force, and they may be welcomed as good news by many: fewer Pap smears. Most women with HPV andor abnormal Pap smear results do not get cervical cancer. Researchers now believe that almost all cervical cancer is caused by HPV 16 and HPV 18. Cervical cancer is diagnosed in 12, 900 women in the United States each year and 4, 400 women die of cervical cancer in. Cervical Cancer Screening: Pap Smear or HPV Test. Elizabeth Stier and Rebecca Perkins, in their report that appears in a June 2014 Annals of Internal Medicine, state that the best route is to undergo BOTH the Pap and HPV. New cervical cancer screening guidelines have been released by the U. Preventative Service Task Force, and they may be welcomed as good news by many: fewer Pap smears. Cervical cancer screening includes two types of screening tests: cytologybased screening, known as the Pap test or Pap smear, and HPV testing. The main purpose of screening with the Pap test is to detect abnormal cells that may develop into cancer if left untreated. New cervical cancer screening guidelines have been released by the U. Preventative Service Task Force, and they may be welcomed as good news by many: fewer Pap smears. Women who have had a total hysterectomy (removal of the uterus and cervix) should stop screening (such as Pap tests and HPV tests), unless the hysterectomy was done as a treatment for cervical precancer (or cancer). The study found that compared with the Pap test, HPV screening significantly increased detection of highgrade precancerous cervical lesions among those who had been vaccinated. What is cervical cancer screening? Cervical cancer screening is used to find changes in the cells of the cervix that could lead to cancer. The cervix is the opening to the uterus and is located at the top of the vagina. Screening includes cervical cytology (also called the Pap test or Pap smear) and, for some women, testing for human papillomavirus (HPV). A new study finds that testing for HPV was linked with significantly fewer cases of precancer in a 48month period compared with using Pap smear testing. Current screening guidelines from the U. Preventive Services Task Force recommend women ages 30 to 65 have a Pap smear every three years, or. It detects the presence of the human papillomavirus, which causes 99 percent of cervical cancer cases; the Pap smear detects the presence of abnormal cells that can indicate cervical cancer or the danger of developing it. Vaccination against HPV is one of the best preventive measures, in addition to regular Pap tests to protect against cervical cancer. The Pap test, or smear, is one of the most reliable. Cervical cancer can be detected at an early stage by using Pap tests. This test is also used for prevention: It can detect cell changes before they develop into a tumor. The HPV test is another way to do screening. Some screening tests aim to detect diseases at an early stage. The pap smear has been one of the greatest public health wins of the past century. Deaths from cervical cancer in the U. 5 per 100, 000 women as a result of the simple screening test. A new screening method for cervical cancer risk may replace the uncomfortable, dreaded Pap smear, according to a study published in JAMA. Testing for cancerrelated human papillomavirus (HPV. The HPV DNA test, paired with routine Pap smears, increases the chances of detecting cervical cancer at an early stage The Pap smear has been used to test. A test for HPV, the virus that causes cervical cancer, works just as well as a Pap smear for finding precancerous changes in women, researchers reported Tuesday. The USPSTF recommends screening for cervical cancer in women age 21 to 65 years with cytology (Pap smear) every 3 years or, for women age 30 to 65 years who want to lengthen the screening interval, screening with a combination of cytology and human papillomavirus (HPV) testing every 5 years. Cotesting for cervical cancer using both Pap smear testing and human papillomavirus (HPV) testing does not improve cancer detection to any great degree in comparison with using HPV testing alone. The Pap test (or Pap smear) looks for precancers, cell changes on the cervix that might become cervical cancer if they are not treated appropriately. The HPV test looks for the virus ( human papillomavirus ) that can cause these cell changes. Once upon a time, cervical cancer screening took place during the annual Pap smear. But the onceannual Pap eventually became the everythreeyears Pap, and now some women won't need to. The Australian Government has updated the cervical cancer screening program for women. Cancer Councils leading experts have come together to explain what this means for you. If you still have questions, you can call Cancer Council on 13 11 20 and speak to one of our specially trained health professionals for free. A cervical screening test (previously known as a smear test) is a method of detecting abnormal cells on the cervix. The cervix is the entrance to the womb from the vagina. Detecting and removing abnormal cervical cells can prevent cervical cancer. The American Cancer Society recommends that women aged 30 to 65 have an HPV test with their Pap test (cotesting) every 5 years to test for cervical cancer. Talk to your health care provider about co. Making Sense of Pap Tests, HPV Tests, and the New Landscape of Cervical Cancer Screening It used to be so simple go for an annual Pap. For generations of women the Pap was a yearly ritual, something of a cultural icon. The USPSTF recommends screening for cervical cancer in women age 21 to 65 years with cytology (Pap smear) every 3 years or, for women age 30 to 65 years who want to lengthen the screening interval, screening with a combination of cytology and human papillomavirus (HPV) testing every 5 years. Previously, the screening for detection of cervical cancer was performed by simple cervicovaginal sample collected by the physician whenever the patient attended the medical consultation, and soon it was established as the annualPap smear. Cervical cancer remains a leading cause of death in many developing countries due to limited screening by Papanicolaou (Pap) smear. We sought to better understand womens beliefs about cervical cancer and screening in Botswana, a middle income African country with high rates of cervical cancer. New USPSTF recommendations say most women can get an HPV test instead of a Pap smear to check for cervical cancer risk, and can wait five years between tests. Cervical Cancer Screening: Pap and HPV Tests. Each year, more than 13, 000 women are diagnosed with cervical cancer in the United States. There are many types of HPV that can cause cervical dysplasia. Most of these types are considered highrisk types, which means that they have been linked with cervical cancer..